Rotator Cuff Repair
When shoulder pain is associated with a rotator cuff tear, ATX Orthopedics, located in Central Austin, can help. Here, Dr. Benjamin Amis can assist to treat rotator cuff injuries in Austin, Texas patients using stretching and strengthening exercises as well as shoulder surgery.
Rotator Cuff Q&A
What is a rotator cuff injury?
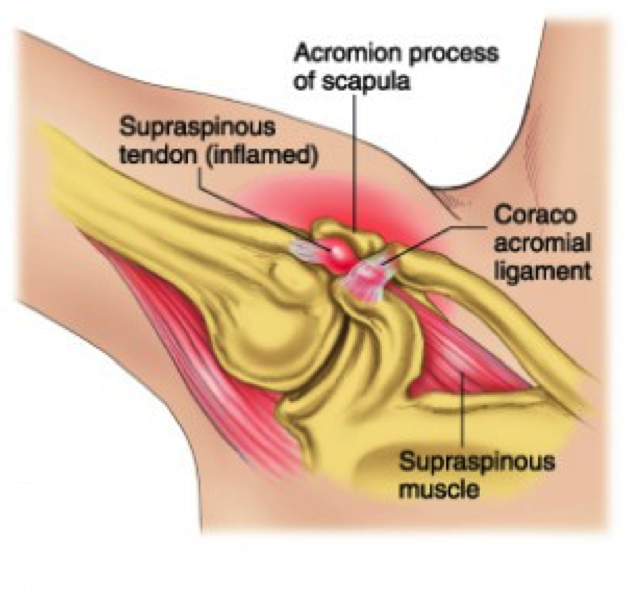
A rotator cuff tear is a common cause of discomfort and disability for many. A torn rotator cuff weakens the shoulder which can make daily activities, such as getting dressed, painful and difficult. When one or more of the rotator cuff tendons has suffered a tear, it will no longer completely attach to the head of the humerus. Frequently, torn tendons will start to fray. As the damage advances, the tendon can tear entirely, occasionally when lifting a heavy item. There are two types:
Partial Tear– the soft tissue is damaged, but not completely severed.
Full-Thickness Tear– also called a complete tear, the soft tissue is split into two pieces.
What causes a rotator cuff tear?
There are two main causes of rotator cuff tears: injury, or acute, and degenerative.
Acute Tear– A fall on an outstretched arm or lifting an overly heavy item with a jerking motion, can tear the rotator cuff. A tear can also occur with a broken collarbone or dislocated shoulder.
Degenerative Tear– Most tears occur because the tendon has worn down over time, common with aging. The dominant arm is usually more susceptible. If you have a degenerative tear in one shoulder, it is more likely to tear the opposite shoulder. Different factors can contribute to degenerative tears such as repeating the same motions over and over again. Baseball, tennis, rowing, and weightlifting can put a person at risk for overuse tears. Additionally, several jobs and chores can cause overuse tears. As a person ages, the blood supply in the tendons also diminishes. This impairs the body’s natural ability to repair it, ultimately leading to a tear. As a person gets older bone spurs can also develop. Lifting the arm causes the tendon to rub on the spur. This is called shoulder impingement. This weakens the tendon, making it even more susceptible to tearing.
What rotator cuff treatments are there?
To treat a rotator cuff injury, the doctor will often begin with non-surgical options such as resting the shoulder, avoiding activities which cause the pain, NSAIDs or other anti-inflammatory drugs, physical therapy and stretching exercises, or steroid injections into the joint. However, when these do not provide adequate relief surgical treatment can be necessary.